This blog is co-authored by Aaron Fu and Kimchav Sov.
The term “digital signature” is often confused and has commonly been described as an e-signature that resembles a hand-drawing signature but applied in digital documents. Indeed, digital signatures provide a highly secure way to implement electronic signatures and play a crucial role in maintaining information security. They provide a way to validate the authenticity, validity and integrity of digital documents. Digital signatures are used in a wide range of applications, including email, contracts, official documents, codes and financial transactions. This blog post will look at many forms of digital signatures and their use cases.
What is a digital signature?
A digital signature is a mathematical code that is attached to an electronic document to verify its authenticity. It is created using a private key that is unique to the signer and can be used to verify that the document was signed by the person who claims to have signed it. Unlike ordinary electronic signatures, which are simply an electronic representation of a handwritten signature (e.g. scanned image of a handwritten signature), digital signatures are based on public-key cryptography, which makes them much more secure.
Digital signatures work by using a combination of public and private keys. The private key is used by the signer to encrypt the document, while the public key is used by the recipient to decrypt it. The public key is freely available to anyone who needs it, while the private key is kept secret by the signer.
What are the Different Types of Digital Signatures and Uses
Cryptographic digital signature
Cryptographic digital signature is a type of digital signature that uses cryptography to authenticate the validity and integrity of a digital document. They are based on asymmetric encryption algorithms, which use private and public keys. The document is signed using the private key and is verified with the public key. Cryptographic digital signatures offer high levels of security and are widely accepted. However, cryptographic digital signatures do not have an inherent mechanism for identity verification that the certificate-based digital signatures offer. They are often used in a variety of applications such as email encryption, code signing, legal document, etc.
Certificate-based digital signature

Certificate-based digital signature is a type of digital signature that uses a digital certificate to verify the identity of the signer. The digital certificate is issued by a trusted third party, known as a certificate authority (CA). These certificates contain information about the signer’s identity and are used to verify the authenticity of the digital signature. Certificate-based digital signatures offer an added level of trust and have a strict Know Your Customer (KYC) process enforced by a CA adhering to regulatory compliance before the issuing of a certificate. They are often used in industries where regulatory compliance and legal requirements are crucial, such as in signing legal documents and contracts.
QR code signature

QR code signature is a type of digital signature that uses a QR code to represent the signature. A unique QR code embedded with a digital signature is generated for each document, containing the necessary information to verify the document. Users scan the QR code using a QR scanner or compatible application to verify the authenticity and integrity of the signature. QR code signatures are used in a variety of applications such as documents, certificates, product authentication statements, and logistics.
Biometric digital signature

Biometric digital signature is a type of digital signature that uses unique physical or behavioural characteristics of an individual such as a fingerprint, facial scan or even handwritten signature to verify the identity of the signer. Biometric signatures offer a high level of security as they are difficult to forge. They are often used in applications where identity verification is critical, such as banking and government documents.
What makes a digital signature secure?

When a document is signed using a digital signature, the signature is embedded into the document itself. This means that if the document is altered in any way, the signature will no longer be valid. This provides a high level of security and ensures that the document cannot be tampered with or forged.
Digital signatures rely on a well-established system called Public Key Infrastructure (PKI) to establish trust and ensure the authenticity of the signatures. In PKI, a certificate authority (CA) is responsible for issuing digital certificates that contain a public key and identifying information about the signer. These digital certificates are used to establish trust between signers and recipients, ensuring that the digital signature is authentic and that the signer is who they claim to be.
What makes a digital signature legally enforceable?

In Singapore, digital signatures are governed by the Electronic Transactions Act (ETA) and the Electronic Transactions (Certification Authority) Regulations (ETCA). These laws provide a legal framework for the use of digital signatures and ensure that they are legally binding and enforceable.
Secure Electronic Signatures (SES) are a specific type of digital signature that is defined in the ETA and provides a legal presumption of authenticity and integrity. This means that if a SES is challenged in court, the court will presume that the signature is authentic and has not been altered unless there is evidence to the contrary. This legal presumption can make it easier for businesses to use electronic signatures, as they can rely on the presumption of authenticity and integrity provided by the ETA.
To qualify as a Secure Electronic Signature, the signature must be created using a method that is uniquely linked to the signatory, such as a digital certificate issued by a recognized CA. In Singapore, CAs are recognized and accredited by the Infocomm Media Development Authority (IMDA), controller of CAs in Singapore. The IMDA is the regulatory body responsible for ensuring that CAs comply with the ETCA, which sets out the requirements for the operation and management of CAs in Singapore.
Of the different types of digital signatures explored earlier, only certificate-based digital signatures qualify as Secure Electronic Signatures.
Who are the recognized CAs in Singapore?
Netrust is Asia’s 1st Public Certificate Authority (CA) and Singapore’s Only Commercial IMDA-accredited CA. Netrust offers a range of digital certificates that are compliant with the ETA and can be used to create Secure Electronic Signatures that are legally binding and admissible as evidence in court.
Netrust is also a member of the Adobe Approved Trust List (AATL) and Microsoft Trusted Root Certificate Program. As such, digital signatures generated by nSignBasic – Netrust Document Signing Certificates, are automatically trusted by Adobe and Microsoft programs. The AATL is a global program that includes a list of trusted digital certificate providers that are recognized by Adobe as meeting certain standards for security and reliability.
By choosing an accredited CA like Netrust, businesses in Singapore can ensure that their digital signatures are reliable and trustworthy and that they comply with the requirements of the ETA and ETCA. This can help to protect businesses from fraud and other types of financial crimes, while also improving their efficiency and productivity in their day-to-day operations.
How can digital signatures help me?

In addition to their security benefits, digital signatures can also help businesses to improve their efficiency and productivity. They eliminate the need for paper-based signatures, which can be time-consuming and expensive. They also provide a fast and efficient way to sign and authenticate documents, which can help to streamline business processes and reduce delays.
For example, digital signatures can be used in the banking and finance industry to sign loan agreements and other financial documents. They can also be used in the legal industry to sign contracts and other legal documents. In the healthcare industry, digital signatures can be used to sign medical records and other important documents.
How can I start using digital signatures?
To use digital signatures in Singapore, businesses must first obtain a digital certificate (such as nSignBasic – Netrust Document Signing Certificates) from a CA like Netrust. Once a business has obtained a digital certificate, they can use it to sign documents using digital signatures. This can be done easily using freely available document readers such as Adobe Reader, or electronic signing workflow solutions such as nSignHub.
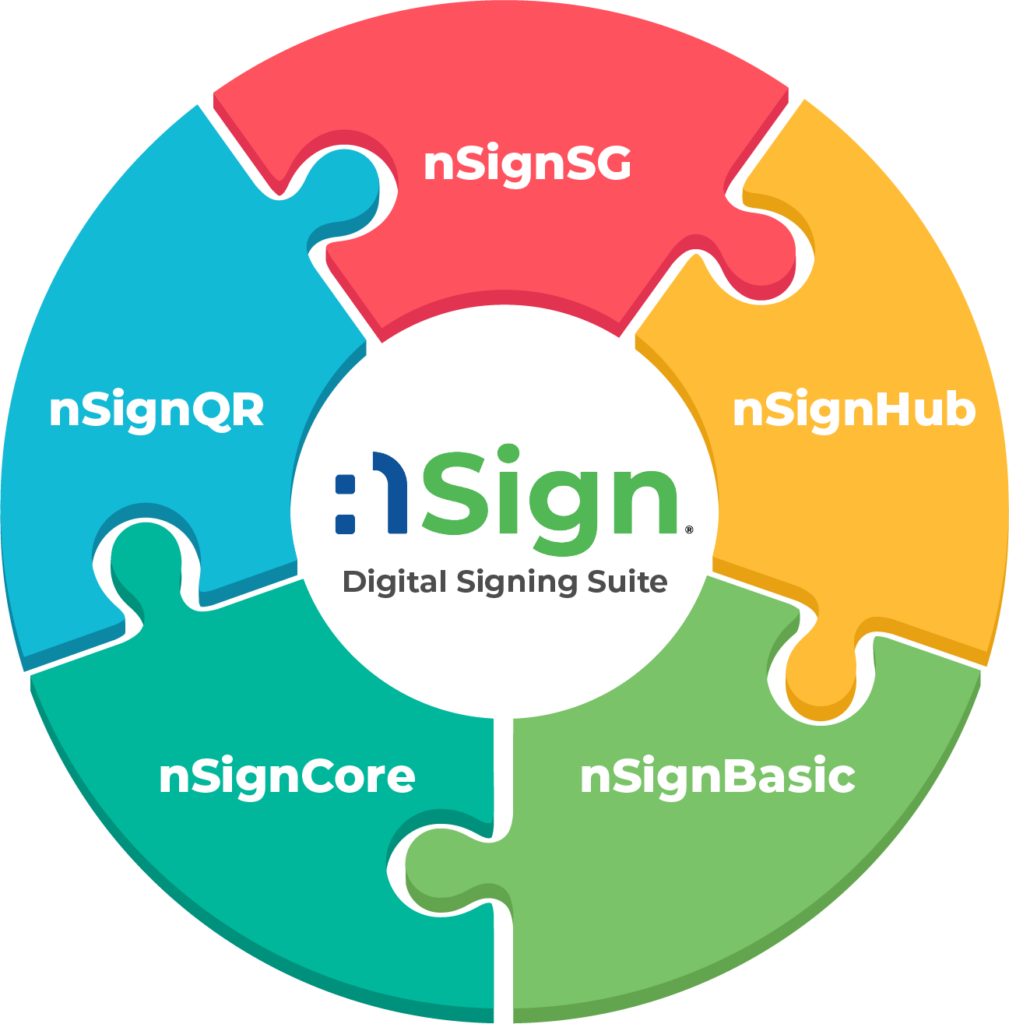
Here at Netrust, we offer a wide range of digital signature solutions to address the needs of business and also day-to-day operations:
- nSignSG: A web-based platform that lets you create digital signatures on PDF documents using Singpass
- nSignHub: A full-fledged electronic workflow solution used to send, sign, track and manage signing processes
- nSignBasic: Document signing certificates (sometimes known as digital certificates or digital IDs) issued by Netrust allow you to add a digital signature to a document to prove the identity of the sender.
- nSignCore: Enable your business applications to perform digital signing via simple-to-integrate REST APIs
- nSignQR: Protect the integrity of your physical documents offline with specially generated QR codes
In conclusion, digital signatures are an important tool for businesses in Singapore. They provide a high level of security and reliability, which can help to protect businesses from fraud. They also provide a fast and efficient way to sign and authenticate documents, which can improve efficiency and productivity. To learn more about how Netrust can help you harness the full potential of electronic signing, visit our website today and request a personalized consultation.
Follow us on LinkedIn for the latest happenings/updates.